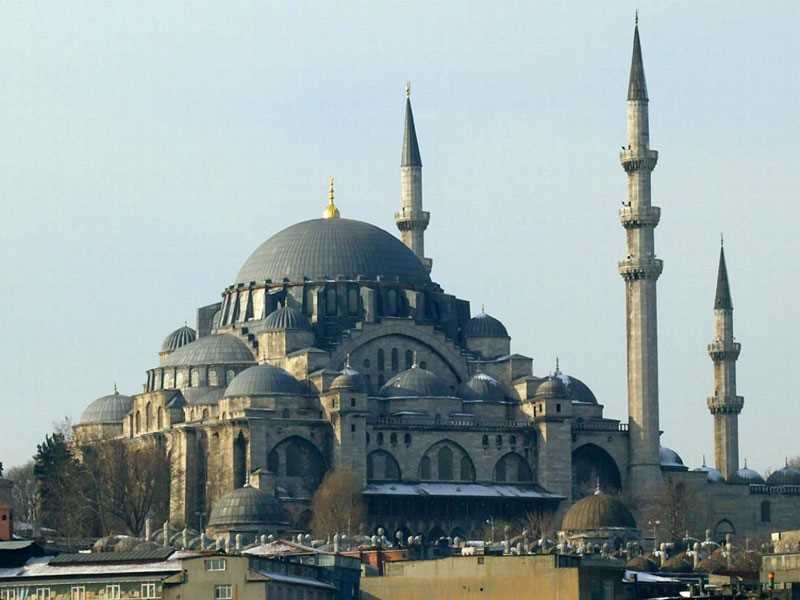
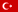
The work of the sultans of the Islamic state after the opening of Constantinople to build the mosques with the best quality, and the finest specifications, depending on the Ottoman architectural style, leaving beautiful effects of the great mosques and distinguished, which has become a landmark of the city of Istanbul. Perhaps one of the most important mosques built after the conquest of Constantinople is the Al-Fateh Mosque, which was ordered by Sultan Muhammad Al-Fatih in 1463 AD and continued until 1470, on the ruins of an ancient Byzantine church that had been destroyed since the Fourth Crusade.
Al Fateh Mosque is situated on one of the seven hills of Istanbul, along the Golden Horn and specifically on Fawzi Pasha Street in the Al Fateh area of the European section of Istanbul.
Atik Sinan was built and built in the form of a complex that includes schools, a library, a hospital, a tourist hostel, a caravan, a primary school, a kitchen that served food for the poor. Tombs or tombs later.
Built in 1771 under the reign of Sultan Mustafa III, the new mosque was designed and built by Sinan Agha. It consists of a central dome with a diameter of 26 m, supported by four small domes on each axis, supported by four Marble columns, adorned with the names of the four caliphs and the names of the Companions who are the missionaries of paradise. Two minarets of this mosque are identical in form, and the pulpit and the linear motifs that surround it are baroque. The mihrab is the same as the old mosque.
The mosque combines two types of Ottoman architecture, due to several seismic disasters, in particular the earthquake of May 22, 1766, which caused the collapse of the mosque's dome to be irreparable and rebuilt.
The courtyard of the mosque is surrounded by many columns and arches, medalled by men, and the southern part of the tomb of Sultan Mohamed El-Fatih is surrounded by a decorated glass wall. The tomb surrounds the walls with Qur'anic verses and a Hadith attributed to the Prophet: "Let Constantinople, .