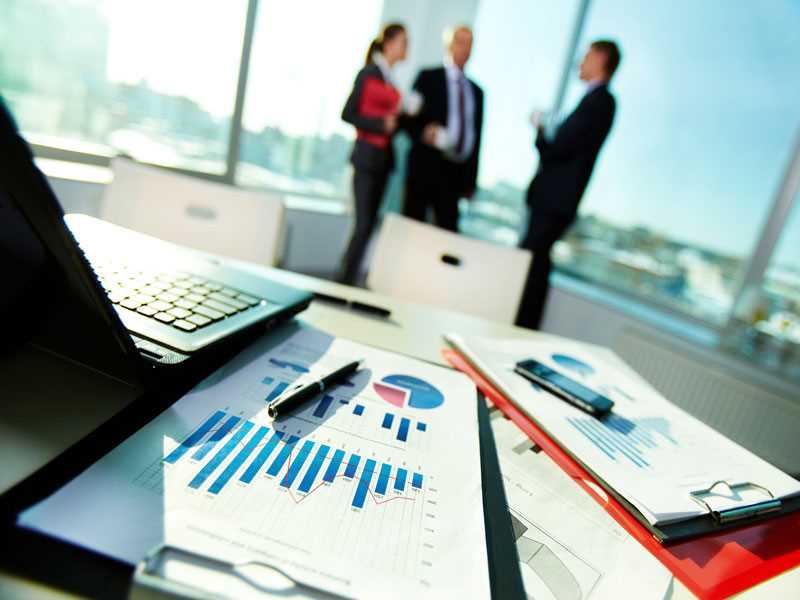
Business Administration is a set of activities that are linked to each other in order to effectively control and control all of the company's functions.
Business Administration is also defined as the processes that are applied in order to activate the interaction with people and objects within the work environment, thus achieving the desired goals successfully.
Other business Administration definitions are actions and methods aimed at directing individuals, business and private business.
The first business school in the world is the Higher School of Commerce in Paris, France, in 1819.
The first business school in the United States was the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania, in 1881. Harvard Business School, founded in 1908.
management jobs
In general, administrators engage in a common set of functions to meet the objectives of the organization. These tasks are described by Henry Foyle as the "Five Elements of Management"
Planning is the advance report of what to do, how to do it, when to do it, and who should do it. It shows the way from the beginning of the organization to what it wants to be. The planning function involves setting goals and arranging a logical order. Administrators are involved in both short-term plans and long-term planning.
Organization involves defining responsibilities to be undertaken, including responsibilities to departments or divisions, and defining organizational relationships. The purpose is to harmonize efforts among all elements in the organization. Coordination should take into account the delegation of authority, responsibility and scope of control within the supervisory units.
Serving teams is to fill important positions with the right people at the right time. It involves identifying staff needs, writing job descriptions, and recruiting and screening people for positions.
Leadership Leading people in a way that achieves the goals of the organization.
This includes the proper allocation of resources and the provision of an effective support system. Orientation requires exceptional personal skills and the ability to motivate people. One critical issue in guidance is finding the right balance between focusing on staff needs and focusing on economic production.
Controlling is the function that assesses quality in all areas and reveals potential or actual deviations in the organization's plan. This ensures high quality performance and satisfactory results while maintaining an organized and problem-free environment. Include monitoring and information management, performance measurement, and the institution of corrective actions.
Budgeting, which is excluded from the above list, includes most SOS functions, with the start of the implementation of the budget plan through the application of budget controls.
Business management is one of the jobs that the labor market needs a lot, and according to the economic need in different business sectors, which contributes to the development of management tools. Therefore, it is based on a range of business management areas,
Management of financial control: One of the most important areas of business management, depends on the need to follow up the financial reports on the work, which contributes to support the monitoring function to follow up the investments, their results, and their impact on the financial budget.
Information management is the functional and technological field that relies on the management of business information, through computers and electronic databases, which are easy to store, retrieve, transfer and deal with.
Operations Management: Oversees the implementation of special operations in the main operational and administrative activities that include sales and purchase, human resources and other administrative divisions.
SUSTAINABILITY MANAGEMENT MANAGEMENT is the management that aims to maintain the sustainability of strategies in the company, maintaining the implementation of administrative programs that help in the continuous development of work.
Operations Management: The Department oversees special operations in all functional divisions. It follows up the formulation of management policies and processes that occur on a daily basis, plans to follow up human resources, coordinates recruitment and recruitment of new employees and contributes to project management and management responsibilities.