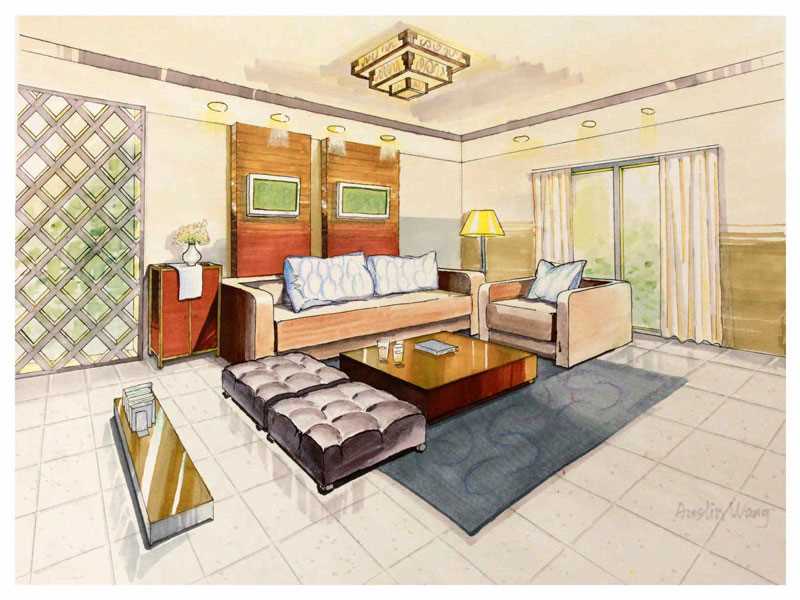
Is a multi-faceted specialization designed to study the internal environment, taking into account tangible and intangible elements to achieve interior design goals. Innovative, functional, and aesthetically pleasing solutions are applied within an architecture to achieve a built-in environment that meets the needs and objectives of users and improves the quality of their lives.
In the internal architecture program, the study depends on the practical application of interior design concepts through a series of design projects. Students learn how to coordinate elements that create well-designed interior spaces, and allow the study of structure, shape, space, materials, fabric, furniture, color and lighting. The design process follows a systematic and coordinated approach (research, analysis and integration of knowledge into the creative process) where internal spaces are created that meet project objectives and meet customer needs and resources.
The requirements of the well-designed interior spaces continue to change and evolve in response to general and commercial needs, advanced and modern technology and social and cultural practices, to take advantage of these changes and developments by encouraging students to explore and develop innovative interior designs to meet these requirements and needs.
The internal architecture program aims at providing students with the knowledge, understanding and skills to respond to future professional challenges through innovative, responsible and sustainable design projects, providing them with a clear understanding of the requirements of the local and international labor market. The program provides an appropriate educational environment including appropriate design studios and computer labs to achieve practical knowledge Advanced technical skills necessary for their practical lives, combined with the philosophical, theoretical and historical appreciation of interior architecture and design.
The BA degree in interior architecture and design is centered around a series of design projects, which evolve according to physical and intellectual complexity, from research, research, development and innovative solutions aimed at making positive changes in the uses of interior spaces.
This degree prepares graduates with the creative and technical skills they need to succeed in their future fields of work. They are diverse and include career opportunities, including but not limited to interior spatial design, residential design, corporate design, sales representative, facility management and care design. Health, sales design, design of hospitality venues, exhibition design, production design (theater, television, film), product design, product design, lighting design, kitchen design and furniture design.
Environmental Design
Environmental design establishes a housing model that meets the requirements of comfort with negative monitoring of the local climate, as a strategy to minimize the use of mechanical machinery, and to maximize the efficiency of positive exchange between construction and the environment.
Modification of internal domestic climate conditions is done by examining the engineering characteristics, local construction technology. Furthermore, the goal of environmental design is to work towards a global policy for the defense of environmental heritage, which is threatened by the effects of development and expansion that have not taken into account local realities.
A thorough study of all climate factors related to the identification and character of the building site, whether in very hot or very cold weather. Is a new approach called environmental design.
The concept of environmental design is deeply related to the awareness that technological progress can be found to reduce environmental sustainability and stop depletion of natural resources.
The main factors that negatively affect the state of the environment stem mostly from the need to eliminate large quantities of non-renewable energy. In this regard, environmental design has a key role in specifically renewing the efficiency of the built-up environment, as the large amount of emissions of polluting gases comes from air conditioning and heating.
In developing countries, the law sets standards for energy saving by controlling maximum permitted consumption in buildings and encouraging the use of renewable resources such as wind and sun.
To reduce environmental impact must first and foremost reduce energy consumption. One of the models that can become a reference point is low-cost housing (due to environmental design), in the case of green building planning, implementation and management.
With the increasing cost of energy and the multitude of laws and technical rules that limit energy consumption in buildings, environmental design has become an irrevocable commitment to all designers because we need to always achieve energy savings.
The development of housing construction has always been filled with the needs of human adaptation to weather conditions, the building, even in its primitive expression, was first a safe haven protected from weather conditions and danger. From the beginning and unconsciously, the relationship between the form and the function of construction has developed, which allowed for a slow but precise evolution towards the present types of architecture. The relationship between structure and energy was also marked by a clear dividing line between classical and modern architecture.
Reasons for the appearance of the design
One of the main reasons for the emergence of the design is:
- • Improving the relationship between building and the environment, says Norbert Schultz, creating the places inhabited by humans by respecting the spirit of the construction site.
- • Improve quality of life and psychological and physical well-being.
- • Conservation of the ecosystem.
- • Use of natural resources (water, vegetation, climate).
- • Non-harmful emissions (smoke, gas, used water and waste).
- • Design flexible buildings for removals, replacements, additions, extensions or changes in use.
- • Provide a wide range of renewable energy sources.
- • Use of environmentally friendly materials and technologies and the priority of local material culture.
Turkey's distinguished universities in the field of interior architecture and environmental design
- • University of Uzegin
- • Tan Bach University (formerly Kimar Borghaz)
- • Peking University
- • Izmir Economic University
University of Istinia
- • Gedek University
- • University of Ashek
- • Istanbul University College
- • University of Cadres Haas
- • Istanbul Commercial University